

19 June 2017.Ģ.“Stereoisomers.” Stereoisomers. The main difference between chiral and achiral is that the mirror image of a chiral is non-superimposable the mirror image of an achiral is superimposable. In order to explain this isomerism of compounds, knowing the chirality of compounds is important because some compounds are chiral while some are achiral. Stereoisomerism is a term which is frequently used in organic chemistry. Rotation of LightĬhiral:Chiral molecules can rotate the plane-polarized light clockwise or anticlockwise.Īchiral:Achiral molecules cannot rotate plane-polarized light in any direction. SuperimpositionĬhiral:The molecule and its mirror image are non-superimposable in chiral molecules.Īchiral: The molecule and its mirror image are superimposable in achiral molecules. Mirror ImageĬhiral: In chiral molecules, a particular molecule and its mirror image are two different compounds.Īchiral: In achiral molecules, the molecule and its mirror image are the same. Difference Between Chiral and Achiral DefinitionĬhiral: Chiral means “asymmetric in such a way that the structure and its mirror image are not superimposable.”Īchiral: Achiral means “symmetric in such a way that it can be superimposed on its mirror image.” SymmetryĬhiral:Chiral molecules are always asymmetric at one or more centers.Īchiral: Achiral molecules are always symmetric at every center. Following image gives a good example.įigure 2: CH3OH is an achiral molecule. This causes the molecule and its mirror image to have distinct properties. But the chemical properties would be sometimes different from each other because the spatial arrangement has a considerable effect on chemical reactions.Ī chiral molecule can have more than one chiral center, which is the carbon atom directly bonded to four different groups. (Most of the physical properties are dependent on the molecular mass). Other physical properties are the same because the molar mass is the same. The compound and the mirror image have the same physical properties except for the direction in which they rotate the polarized light.

Therefore, the mirror image of this kind of molecules is not identical and are considered as two different molecules. The enantiomer of a compound has the same structure of the molecule, but the spatial arrangement is different. The mirror images of chiral compounds are known as enantiomers. Chirality may occur in both organic and inorganic compounds.
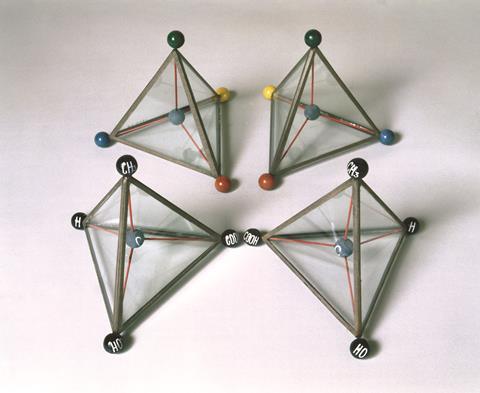
It belongs to the category of stereoisomerism. The presence of different mirror images is known as isomerism.

For example, if a carbon atom in a molecule has four different groups attached to it, it is chiral. In order to be chiral, a molecule should have an asymmetric carbon atom. Key Terms: Achiral, Achiral Molecules, Chiral, Chirality, Chiral Carbon, Chiral Center, Enantiomers, Isomerism What is ChiralĪ chiral molecule is asymmetric in such a way that the structure and its mirror image are not superimposable. What is the difference between Chiral and Achiral The main difference between chiral and achiral is that the mirror image of a chiral is non-superimposable whereas the mirror image of an achiral is superimposable. A chiral carbon is an asymmetric carbon atom present in a compound. Chiral carbon is the main feature that can be used in order to determine the chirality of a molecule. Chirality is a term used to describe whether the mirror image of a compound is superimposable with that compound or not.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
